Evidence-based management entails making decisions and creating organizational practices that are informed by analyzing the best available data. The practice of evidence-based decision making in management (often abbreviated as EBMgt) evolved from medicine and emphasizes a rational, objective, and empirical approach to addressing business issues. It is analogous to the scientific method which uses experiments and data collection to advance knowledge.
Evidence-Based Management
EBMgtis the practice of making organizational decisions that incorporates the conscientious use of both scientific and organizational facts combined 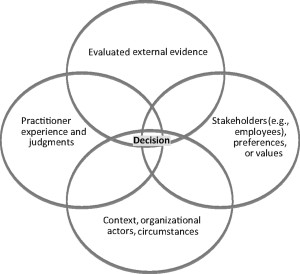 with the development of professional expertise and ethical judgment (e.g., implications for stakeholders). Results of EB practice are improved decision quality through more consistent use of practices that work.
with the development of professional expertise and ethical judgment (e.g., implications for stakeholders). Results of EB practice are improved decision quality through more consistent use of practices that work.
Companies with a culture of evidence-based decision making ensure that all decision makers have performance data at their fingertips every day. They also follow four practices:
- They establish one undisputed source of performance data;
- They give decision makers at all levels near-real-time feedback;
- They consciously articulate their business rules and regularly update them in response to facts;
- And they provide high-quality coaching to employees who make decisions on a regular basis.
Evidence-Based Medicine
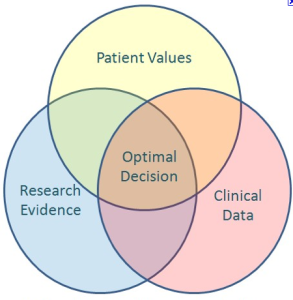 Evidence-based medicine is not cookbook medicine. It means pairing your clinical judgment with the relevant scientific evidence and including your patients’ values and preferences into making a decision for your patient. It’s about individualizing therapy. The most common definition of EBM is taken from Dr. David Sackett. EBM is “the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of the individual patient. It means integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence from systematic research.” (Sackett D, 1996)
Evidence-based medicine is not cookbook medicine. It means pairing your clinical judgment with the relevant scientific evidence and including your patients’ values and preferences into making a decision for your patient. It’s about individualizing therapy. The most common definition of EBM is taken from Dr. David Sackett. EBM is “the conscientious, explicit and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of the individual patient. It means integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence from systematic research.” (Sackett D, 1996)
The evidence, by itself, does not make a decision for you, but it can help support the patient care process. The full integration of these three components into clinical decisions enhances the opportunity for optimal clinical outcomes and quality of life. The practice of EBM is usually triggered by patient encounters which generate questions about the effects of therapy, the utility of diagnostic tests, the prognosis of diseases, or the etiology of disorders.
Evidence-Based Management in Software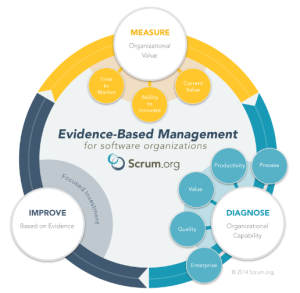
Evidence-Based Management (EBMgt™) is an approach to managing software organizations for the value they deliver to the organization as a whole. It relies on the evaluation of valuable outcomes for the company and determines which parts of the software delivery process contribute to them. This helps focus investments to areas of high-impact first and provides a framework for reevaluating their success in short-cycles.
The survival and prosperity of organizations depending on software products highly depends on the value they deliver with their services. If no evidence is collected on value, informed decisions cannot be made to optimize it. Only upon evidence, are informed management decisions possible regarding the addition, revision and removal of organizational practices that influence the organization’s value.
Evidence over the delivered value, and the ability to deliver value, is captured under the form of metrics in 3 categories:
- Time to market
- Value
- Ability to innovate
Source:


